Infusion Pumps: Delivering Medications with Precision and Safety
Introduction:
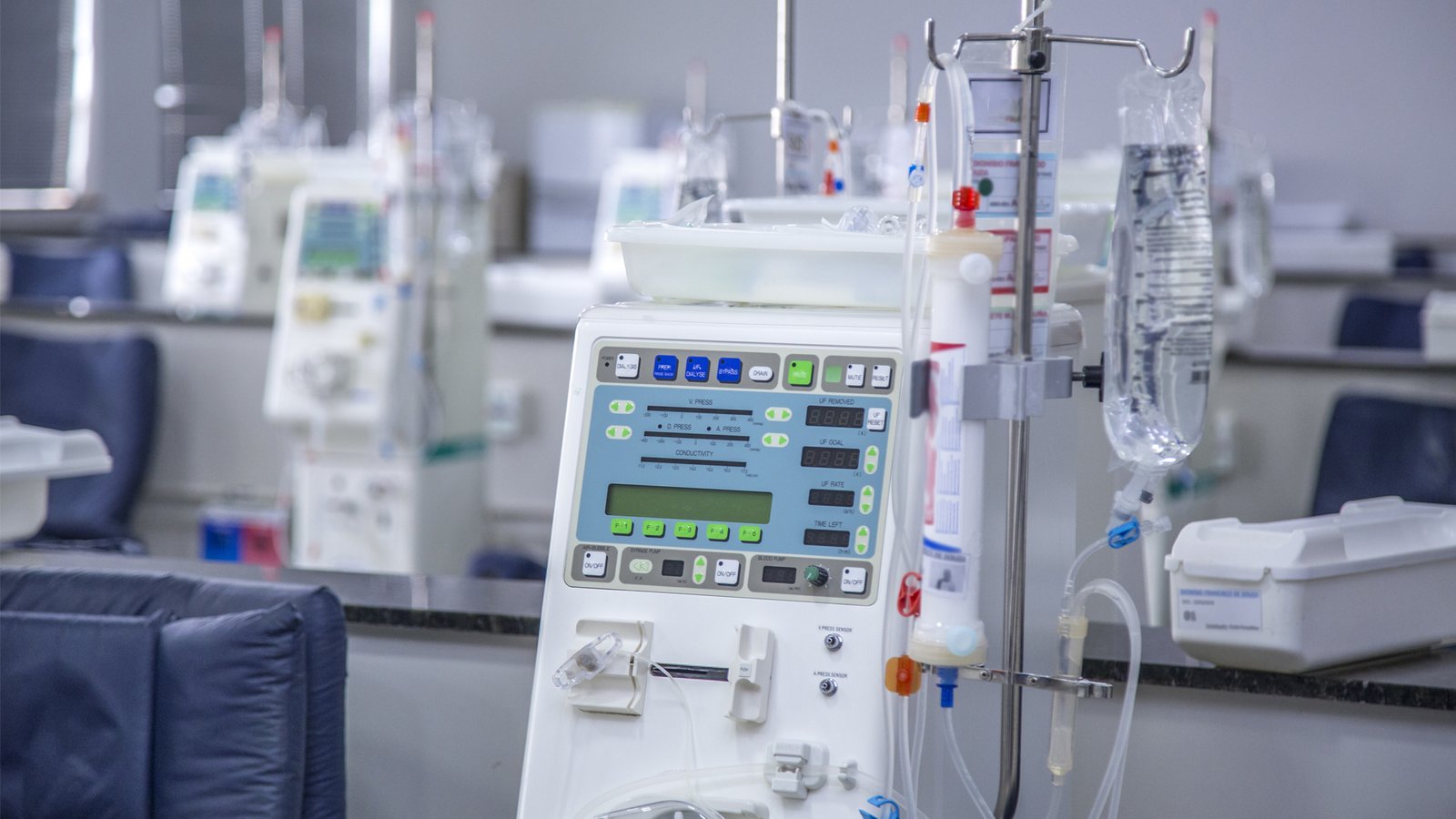
Infusion pumps are essential medical devices used to deliver fluids, medications, and nutrients to patients in a controlled and precise manner. These devices play a critical role in modern healthcare, ensuring accurate dosing, continuous delivery, and patient safety. This article explores the importance of infusion pumps, their functionality, different types, safety features, and their impact on improving patient care.
The Significance of Infusion Pumps:
Infusion pumps are crucial in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and home care. They enable healthcare providers to administer fluids, medications, blood products, and nutrition to patients at a controlled rate and with high accuracy. Infusion pumps eliminate the need for manual administration, ensuring precise dosing and continuous delivery.
Functionality of Infusion Pumps:
Infusion pumps operate by utilizing a motor-driven mechanism that propels fluids through tubing and into the patient’s bloodstream. The pump’s speed and flow rate can be adjusted according to the prescribed dosage and therapy requirements. Some pumps also offer additional features, such as programmable infusion profiles and smart alarms to enhance safety and efficiency.
Types of Infusion Pumps:
a. Volumetric Infusion Pumps: These pumps deliver fluids and medications in precise volumes over a specific time period. They are commonly used for intravenous (IV) therapies, including antibiotics, pain medications, and chemotherapy drugs.
b. Syringe Infusion Pumps: Syringe pumps are designed to deliver medications or fluids from a syringe at a controlled rate. They are frequently used for critical care settings, neonatal care, and situations that require highly accurate dosing.
c. Ambulatory Infusion Pumps: Ambulatory pumps are portable devices that allow patients to receive infusion therapy outside of the hospital setting. They provide flexibility and mobility for patients who require long-term therapies or infusion at home.
Safety Features and Patient Care:
a. Dose Error Reduction Systems: Modern infusion pumps incorporate advanced safety features, such as dose error reduction systems (DERS), which help prevent medication errors. These systems can detect programming errors, drug incompatibilities, and potential adverse events, ensuring patient safety.
b. Alarm Systems: Infusion pumps are equipped with alarm systems to alert healthcare providers in case of occlusion, air bubbles, low battery, or any other irregularities. Timely alarms help prevent interruptions in therapy and ensure prompt intervention.
c. Integrated Databases: Some infusion pumps can integrate with electronic health record systems, allowing for seamless documentation and monitoring of infusion therapy. This promotes accurate medication reconciliation, reduces manual errors, and facilitates comprehensive patient care.
Impact on Patient Care:
a. Accurate Medication Delivery: Infusion pumps ensure precise dosing and continuous delivery of medications, minimizing the risk of medication errors and improving patient safety.
b. Optimal Fluid Management: Infusion pumps enable healthcare providers to administer fluids and maintain fluid balance accurately, especially in critical care settings and surgical procedures.
c. Enhanced Therapy Efficiency: With infusion pumps, healthcare providers can optimize therapy regimens, adjust dosages, and customize infusion profiles to meet individual patient needs. This leads to improved treatment outcomes and patient comfort.
Conclusion:
Infusion pumps are indispensable medical devices that provide precise and controlled delivery of fluids, medications, and nutrients to patients. Their functionality, safety features, and diverse types contribute significantly to improving patient care in various healthcare settings. Infusion pumps ensure accurate dosing, continuous infusion, and enhanced therapy efficiency, leading to improved patient outcomes and increased patient safety. As technology advances, infusion pumps will continue to evolve, incorporating more advanced features to further enhance their functionality and contribute to optimal patient care.